Get ready to dive into the world of retirement planning for self-employed individuals. Buckle up as we explore the unique challenges, different savings options, investment strategies, and financial considerations that can help you pave the way to a comfortable retirement.
Overview of Retirement Planning for Self-Employed Individuals
Retirement planning is essential for self-employed individuals to ensure financial security and stability in their later years. Unlike those with traditional employment, self-employed individuals face unique challenges when it comes to preparing for retirement. They must take on the responsibility of funding their retirement accounts without the assistance of an employer. This requires careful planning and discipline to build a sufficient nest egg for the future.
Importance of Retirement Planning for Self-Employed Individuals
Retirement planning allows self-employed individuals to maintain their desired lifestyle and cover expenses once they stop working. Without a traditional employer-sponsored retirement plan, self-employed individuals must proactively save and invest for their retirement years. By starting early and consistently contributing to retirement accounts, they can build a solid financial foundation for the future.
Challenges Faced by Self-Employed Individuals in Retirement Planning
Self-employed individuals often have fluctuating income levels, making it challenging to set aside a fixed amount for retirement savings. They may also lack access to employer-sponsored retirement plans, such as 401(k) or pension plans, which offer matching contributions. Additionally, self-employed individuals must navigate complex tax regulations and choose the most suitable retirement accounts to maximize their savings while minimizing taxes.
Retirement Options for Self-Employed Individuals
Self-employed individuals have several retirement options to choose from, such as SEP-IRA, Solo 401(k), SIMPLE IRA, and Keogh plans. These plans offer tax advantages and flexibility in contribution limits, allowing self-employed individuals to tailor their retirement savings strategy to their specific needs and goals. By exploring these retirement options and consulting with a financial advisor, self-employed individuals can create a comprehensive retirement plan that aligns with their long-term financial objectives.
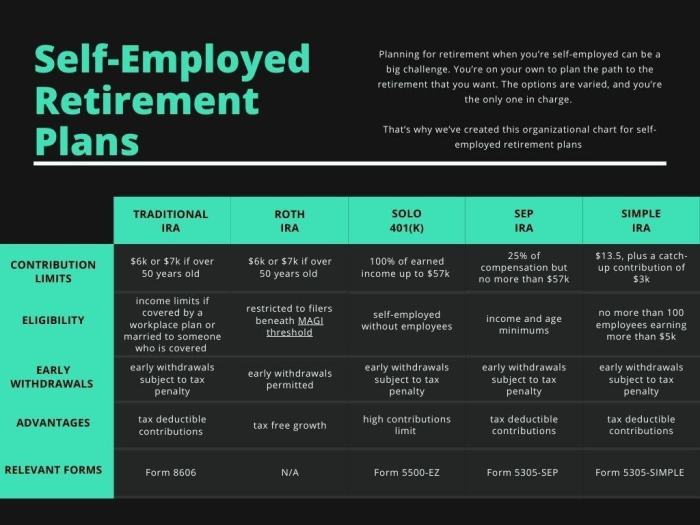
Retirement Savings Options for Self-Employed Individuals
When it comes to retirement savings, self-employed individuals have several options to choose from. Each plan comes with its own set of rules, contribution limits, eligibility requirements, and tax implications. Let’s take a closer look at some of the most popular retirement savings options for self-employed individuals.
SEP-IRA (Simplified Employee Pension IRA)
SEP-IRA is a retirement plan that allows self-employed individuals to contribute up to 25% of their net earnings from self-employment, up to a maximum of $58,000 in 2021. Contributions are tax-deductible, and the earnings grow tax-deferred until withdrawal. One of the main advantages of a SEP-IRA is its high contribution limit, making it an attractive option for self-employed individuals with higher income levels. However, it does not allow for catch-up contributions for individuals over 50.
Solo 401(k)
A Solo 401(k), also known as an Individual 401(k) or Self-Employed 401(k), is a retirement plan designed for self-employed individuals with no employees other than a spouse. It allows for both employer and employee contributions, with a maximum total contribution of $58,000 (or $64,500 for individuals over 50) in 2021. Solo 401(k) offers higher contribution limits than a SEP-IRA and allows for catch-up contributions for individuals over 50. However, it requires more administrative work and may involve higher fees.
SIMPLE IRA (Savings Incentive Match Plan for Employees)
A SIMPLE IRA is a retirement plan that allows self-employed individuals and small business owners to contribute up to $13,500 (or $16,500 for individuals over 50) in 2021, with a mandatory employer match of up to 3% of the employee’s compensation. Contributions are tax-deductible, and earnings grow tax-deferred until withdrawal. The main advantage of a SIMPLE IRA is its simplicity and lower administrative costs compared to other retirement plans. However, it has lower contribution limits than SEP-IRA and Solo 401(k).
Investment Strategies for Self-Employed Retirement Planning
When it comes to planning for retirement as a self-employed individual, maximizing your savings through smart investment strategies is crucial. By strategically allocating your funds, you can set yourself up for a comfortable retirement.
Importance of Diversification in Self-Employed Retirement Portfolios
Diversification is key to reducing risk and optimizing returns in your retirement portfolio. By spreading your investments across different asset classes such as stocks, bonds, and real estate, you can protect your savings from market fluctuations. This strategy helps ensure that you are not overly exposed to the risks of any single investment.
- Diversifying your portfolio can help you achieve a balance between risk and return.
- Consider investing in a mix of assets to minimize the impact of market volatility on your retirement savings.
- Regularly review and rebalance your portfolio to maintain diversification and adapt to changing market conditions.
Risk Tolerance Levels for Self-Employed Individuals
Understanding your risk tolerance is crucial when investing for retirement as a self-employed individual. Your risk tolerance determines how much volatility you can handle in your investment portfolio. Factors such as your age, financial goals, and comfort with risk all play a role in determining your risk tolerance level.
It’s important to strike a balance between taking on enough risk to grow your savings and avoiding excessive risk that could jeopardize your retirement goals.
- Assess your risk tolerance by considering how you would react to market downturns or fluctuations.
- Consult with a financial advisor to determine an appropriate investment strategy based on your risk tolerance and financial objectives.
- Regularly reassess your risk tolerance as your financial situation and retirement goals evolve over time.
Financial Planning Considerations for Retirement
When it comes to planning for retirement as a self-employed individual, there are several key financial considerations to keep in mind. By creating a retirement budget, setting financial goals, managing cash flow effectively, and considering the role of emergency funds and insurance, you can ensure a more secure financial future.
Creating a Retirement Budget and Setting Financial Goals
One of the first steps in retirement planning is to establish a detailed budget that Artikels your current expenses and projected retirement needs. By setting financial goals, you can determine how much you need to save each month to reach your desired retirement income.
Managing Cash Flow Effectively
Managing cash flow is essential for self-employed individuals to ensure consistent retirement savings contributions. By tracking your income and expenses closely, you can identify areas where you can cut costs or increase revenue to boost your retirement savings.
The Role of Emergency Funds and Insurance
Building an emergency fund is crucial for self-employed individuals, as it can provide a financial safety net in case of unexpected expenses or fluctuations in income. Additionally, having adequate insurance coverage, such as health insurance and disability insurance, can help protect your retirement savings from unforeseen risks.
