Yo, listen up! We’re about to dive into the world of credit reports. Get ready to learn all about this crucial aspect of your financial life with a fresh and engaging twist.
Now, let’s break it down for you in a way that’s easy to understand.
Overview of Credit Reports
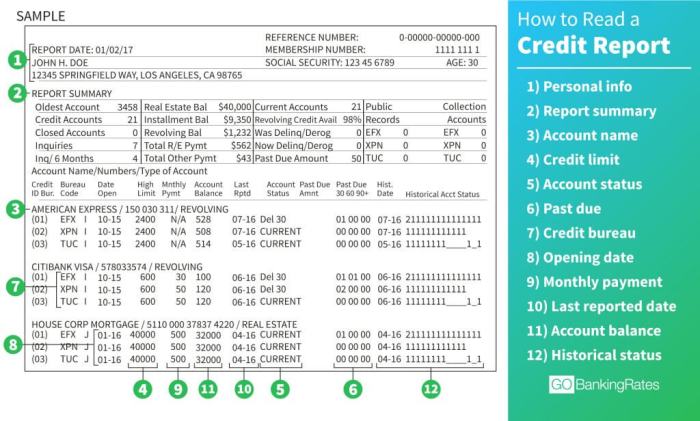
A credit report is a detailed record of an individual’s credit history, including their borrowing and repayment activities. It is used by lenders, employers, and landlords to assess an individual’s creditworthiness and financial responsibility.
Key Components of a Credit Report
- Credit Score: A numerical representation of an individual’s creditworthiness, typically ranging from 300 to 850.
- Credit History: A detailed account of the individual’s past borrowing and repayment behavior.
- Public Records: Information on bankruptcies, tax liens, and civil judgments that may impact creditworthiness.
- Credit Inquiries: Records of entities that have requested the individual’s credit report.
Uses of Credit Reports
Lenders use credit reports to determine whether to approve a loan or credit application and to set interest rates. Employers may review credit reports as part of the background check process to assess financial responsibility. Landlords use credit reports to evaluate a potential tenant’s ability to pay rent on time.
Obtaining and Reading a Credit Report
When it comes to your credit report, it’s crucial to know how to get your hands on it and understand what it’s telling you. Let’s break down the process of obtaining and reading a credit report in detail.
Obtaining a Free Credit Report
One way to obtain a free credit report is through AnnualCreditReport.com, which is the only official site authorized by federal law for this purpose. You are entitled to one free credit report from each of the three major credit bureaus (Equifax, Experian, and TransUnion) every 12 months.
Another method is to check with your credit card issuer or financial institution, as some of them offer free credit report access to their customers.
Reading and Interpreting a Credit Report
When you receive your credit report, pay attention to details such as personal information, account history, credit inquiries, and public records. Make sure all the information is accurate and up to date.
Look at your credit score, which is a numerical representation of your creditworthiness. The higher the score, the better your credit standing.
Review any negative items on your report, such as late payments, collections, or bankruptcies. Understand how these factors can impact your overall credit health.
Common Errors on a Credit Report
Common errors that may appear on a credit report include inaccurate personal information, duplicate accounts, incorrect payment history, and fraudulent activity. It’s important to dispute any errors you find to ensure your credit report is correct.
Keep an eye out for identity theft red flags, such as accounts you didn’t open or unfamiliar inquiries. Report any suspicious activity immediately to protect your credit.
Factors Impacting Credit Scores
When it comes to credit scores, there are several key factors that can have a significant impact on your overall score. Understanding these factors is crucial for managing your credit effectively and improving your financial health.
Payment History
Your payment history is one of the most important factors that influence your credit score. Making timely payments on your credit accounts, loans, and bills can have a positive impact on your score. On the other hand, missing payments or making late payments can significantly lower your score. It is essential to prioritize paying your bills on time to maintain a healthy credit score.
Credit Utilization Ratio
Another critical factor that affects your credit score is your credit utilization ratio. This ratio compares the amount of credit you are using to the total amount of credit available to you. Keeping this ratio low, ideally below 30%, can help improve your credit score. High credit utilization can signal to lenders that you may be overextended financially.
Length of Credit History
The length of your credit history also plays a role in determining your credit score. Lenders like to see a long history of responsible credit use, as it demonstrates your ability to manage credit over time. If you are new to credit, it may take some time to build a solid credit history and improve your score.
Types of Credit in Use
The types of credit accounts you have can impact your credit score as well. Having a mix of credit, such as credit cards, installment loans, and a mortgage, can demonstrate that you can manage different types of credit responsibly. However, it is essential to only take on credit that you need and can manage effectively.
New Credit Inquiries
Finally, the number of new credit inquiries on your credit report can also affect your credit score. When you apply for new credit, lenders will typically pull your credit report, resulting in a hard inquiry. Too many hard inquiries in a short period can lower your score, as it may indicate to lenders that you are taking on too much new debt.
Credit Report Monitoring and Protection
Regularly monitoring your credit report is crucial to staying informed about your financial health. By keeping an eye on your credit report, you can quickly spot any errors, unauthorized activity, or signs of identity theft.
Identity theft can wreak havoc on your credit report by damaging your credit score and making it harder for you to access loans or credit cards in the future. To protect yourself against identity theft, consider taking the following steps:
– Regularly review your credit report for any suspicious activity or inaccuracies.
– Set up fraud alerts with the credit bureaus to be notified of any unusual credit activity.
– Consider freezing your credit report to prevent unauthorized access to your credit information.
– Use strong, unique passwords for your financial accounts and enable two-factor authentication whenever possible.
There are various resources and services available to help you monitor and protect your credit report. Some options include:
– Credit monitoring services that provide regular updates on your credit report and alert you to any changes.
– Identity theft protection services that offer additional layers of security to safeguard your personal information.
– Free credit report websites where you can access your credit report from all three major credit bureaus for free once a year.
By staying vigilant and taking proactive steps to monitor and protect your credit report, you can help ensure your financial well-being and safeguard your personal information from identity theft.
