With loan default consequences at the forefront, this paragraph opens a window to an amazing start and intrigue, inviting readers to embark on a storytelling journey filled with unexpected twists and insights.
When it comes to financial agreements, the repercussions of defaulting on a loan can be game-changing. Let’s dive into the world of loan default consequences and explore what borrowers need to know.
Overview of Loan Default Consequences
When it comes to financial agreements, loan default refers to the failure of a borrower to repay the loan according to the agreed terms. This can happen due to various reasons such as financial difficulties, job loss, or unexpected expenses.
Types of Loans at Risk
- Student Loans: Defaulting on student loans can lead to wage garnishment, damaged credit score, and even legal action by loan providers.
- Mortgages: Defaulting on a mortgage can result in foreclosure, where the lender takes possession of the property due to non-payment.
- Personal Loans: Defaulting on a personal loan can also damage your credit score and make it harder to borrow in the future.
Implications of Loan Default
Defaulting on a loan can have serious consequences for borrowers. It can lead to a damaged credit score, making it difficult to secure loans in the future. Additionally, lenders may take legal action to recover the unpaid amount, which can result in wage garnishment or asset seizure.
Legal Ramifications
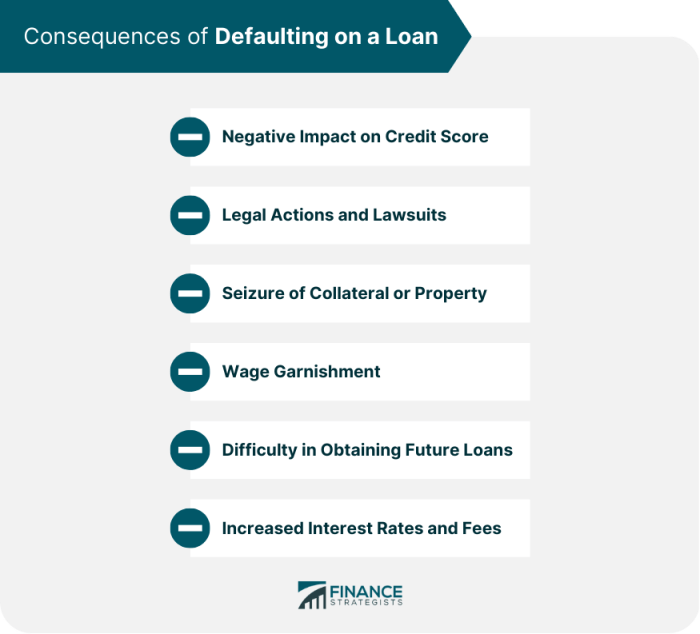
In the unfortunate event of a loan default, borrowers can face serious legal consequences that can have a long-lasting impact on their financial well-being. Lenders have the right to pursue legal action against defaulting borrowers in order to recover the outstanding debt.
Legal Consequences
- Borrowers may be sued by the lender in civil court for the amount owed, including any accrued interest and legal fees.
- If a judgment is entered against the borrower, the lender may be able to garnish wages, seize assets, or place liens on property to satisfy the debt.
- In extreme cases, borrowers may even face bankruptcy proceedings if they are unable to repay the loan amount.
Impact on Credit Score
Loan default can have a devastating impact on the borrower’s credit score. A default will be reported to credit bureaus, resulting in a significant drop in the borrower’s credit score.
Defaulting on a loan can stay on a borrower’s credit report for up to seven years, making it difficult to obtain credit or loans in the future.
Having a low credit score can also affect the borrower’s ability to secure housing, employment, or favorable interest rates on future loans.
Financial Penalties and Fees
When a borrower defaults on a loan, they can expect to face a slew of financial penalties, fees, and interests that can significantly add to their debt.
Accruing Costs
Following a loan default, the borrower may encounter the following financial consequences:
- Penalties for missed payments: Lenders often charge a fee for each missed payment, which can quickly add up.
- Increased interest rates: Defaulting on a loan can trigger higher interest rates, causing the overall debt to grow faster.
- Collection fees: If the lender sends the loan to collections, the borrower may be responsible for additional fees associated with the collection process.
Escalating Debt
These additional costs can escalate the borrower’s debt in a number of ways:
- Compound interest: Unpaid interest can compound over time, leading to a ballooning debt that can be difficult to manage.
- Extended repayment terms: Some lenders may extend the repayment terms of the loan to accommodate the added fees and penalties, further prolonging the debt repayment process.
Mitigating Strategies
Despite the financial consequences of defaulting on a loan, borrowers can take steps to negotiate or mitigate these costs:
- Communication with the lender: Open communication with the lender about the financial difficulties that led to the default can sometimes result in a more lenient repayment plan.
- Seeking legal advice: Consulting with a financial advisor or attorney can help borrowers understand their rights and explore options for resolving the debt.
- Debt settlement: In some cases, borrowers may be able to negotiate a settlement with the lender, agreeing to pay a reduced amount to satisfy the debt.
Asset Seizure and Repossession
Defaulting on certain types of loans can have serious consequences, including asset seizure and repossession. When a borrower fails to make payments as agreed, lenders have the legal right to claim and repossess assets to recoup their losses. This process can vary depending on the type of loan and the laws governing it.
Types of Assets at Risk
Various assets may be at risk of seizure or repossession in the event of default. Some common examples include:
- Automobiles
- Real estate properties
- Jewelry
- Electronics
- Boats or recreational vehicles
Legal Process of Asset Repossession
Lenders typically have to follow a legal process to claim and repossess assets from defaulting borrowers. This process may involve sending notices of default, providing opportunities for borrowers to catch up on payments, and obtaining court orders for repossession.
Once a lender legally repossesses an asset, they may sell it to recover the outstanding debt. In some cases, borrowers may still be liable for any remaining balance after the sale of the asset.
