Yo, listen up! Interest rates and mortgages are about to drop some serious knowledge on you. Get ready to dive into a world where money talks and loans walk, all while keeping it real and relatable.
So, buckle up as we break down the relationship between interest rates and mortgage rates, how they impact your payments, and the key factors influencing these rates in the market. It’s about to get lit!
Overview of Interest Rates and Mortgages
Interest rates and mortgage rates are like peanut butter and jelly – they go hand in hand. Mortgage rates are directly influenced by interest rates set by the Federal Reserve.
Impact of Interest Rates on Mortgage Payments
When interest rates go up, mortgage payments go up like Drake’s music on the charts. This means borrowers end up paying more in interest over the life of the loan. On the flip side, when interest rates drop, mortgage payments can decrease, giving borrowers a little more cash in their pockets.
Examples of Interest Rate Changes on Borrowing Costs
- When interest rates rise by 1%, a borrower might end up paying thousands of dollars more in interest over a 30-year mortgage. It’s like going from shopping at the Dollar Store to splurging at Gucci.
- Conversely, if interest rates drop by 0.5%, a borrower could potentially save money on their monthly mortgage payments. It’s like finding a killer sale at your favorite store.
Factors Influencing Interest Rates
When it comes to interest rates in the mortgage market, there are several key factors that come into play. These factors can influence how rates fluctuate and impact borrowers looking to secure a mortgage.
Economic Indicators
- The state of the economy: When the economy is strong, interest rates tend to rise as borrowing becomes more expensive. Conversely, in a weak economy, rates may be lower to stimulate borrowing and spending.
- Inflation rates: High inflation rates can lead to higher interest rates to offset the decrease in purchasing power of the currency.
- Employment rates: Low unemployment rates typically signal a strong economy, which may result in higher interest rates. Conversely, high unemployment rates could lead to lower rates to encourage spending.
Central Banks Role
- Central banks, such as the Federal Reserve in the United States, play a crucial role in setting interest rates. They use tools like the federal funds rate to influence borrowing costs for banks, which in turn affects the rates offered to consumers.
- By adjusting these key interest rates, central banks can control inflation, spur economic growth, or combat recession.
- Market expectations and central bank announcements can also impact interest rates, as investors react to changes in monetary policy and economic outlook.
Types of Mortgages
When it comes to mortgages, there are different types to choose from based on your financial goals and preferences. Two common types are fixed-rate mortgages and adjustable-rate mortgages.
Fixed-Rate Mortgages vs. Adjustable-Rate Mortgages
Fixed-rate mortgages have a set interest rate that remains constant throughout the life of the loan, providing stability in monthly payments. On the other hand, adjustable-rate mortgages have interest rates that can fluctuate based on market conditions, leading to potential changes in monthly payments.
Interest Rate Structure for Various Mortgage Types
For fixed-rate mortgages, the interest rate is determined at the beginning and remains unchanged. In contrast, adjustable-rate mortgages often have an initial fixed period with a lower interest rate, followed by adjustments based on a specific index.
Beneficial Scenarios for Each Type of Mortgage
– Fixed-rate mortgages are beneficial for those who prefer predictable payments and plan to stay in their homes long-term.
– Adjustable-rate mortgages may be beneficial for individuals who expect to sell or refinance before the initial fixed period ends or anticipate interest rates decreasing in the future.
Impact of Credit Scores on Mortgage Rates
Credit scores play a significant role in determining the interest rates offered on mortgages. Lenders use credit scores to assess the risk of lending money to individuals, with higher credit scores typically qualifying for lower interest rates. Here’s how credit scores affect mortgage rates and strategies for improving them to secure better rates.
Effect of Credit Scores on Interest Rates
- Lenders consider credit scores as a reflection of an individual’s creditworthiness. Higher credit scores indicate responsible financial behavior, making borrowers less risky for lenders.
- Borrowers with excellent credit scores (generally above 750) are likely to qualify for the lowest interest rates on mortgages, saving significant amounts over the life of the loan.
- On the contrary, individuals with lower credit scores may face higher interest rates or may even struggle to qualify for a mortgage due to perceived higher risk.
Strategies to Improve Credit Scores
- Make timely payments on existing debts, such as credit cards, loans, and utilities, to demonstrate financial responsibility.
- Reduce outstanding debt levels to lower credit utilization ratios, which can positively impact credit scores.
- Regularly check credit reports for errors or inaccuracies and address them promptly to ensure an accurate representation of creditworthiness.
Variation in Interest Rates Based on Creditworthiness
- Borrowers with excellent credit scores may qualify for interest rates that are significantly lower than those with average or poor credit scores.
- Even a small difference in interest rates can result in substantial savings over the life of a mortgage, making it crucial for borrowers to strive for higher credit scores.
- Lenders may offer different interest rate tiers based on credit scores, with the best rates reserved for those with the highest creditworthiness.
Mortgage Rate Trends
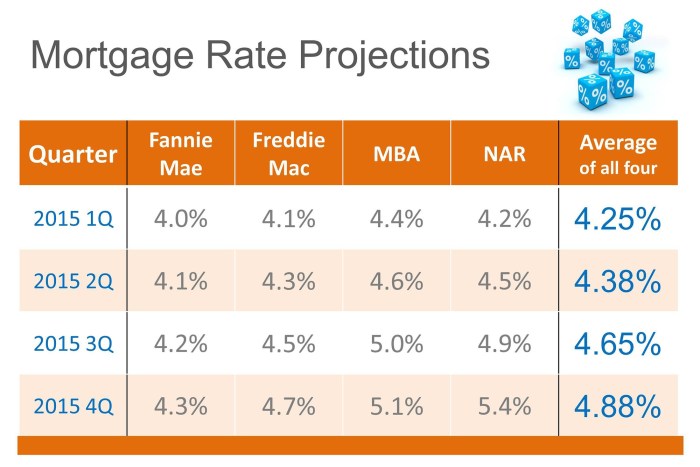
When it comes to mortgage rate trends, it’s important to look back at historical data to understand how rates have fluctuated over the past decade.
Historical Trends
Over the past ten years, mortgage rates have experienced both highs and lows. Following the 2008 financial crisis, rates hit record lows, prompting a surge in home buying and refinancing. However, as the economy recovered, rates began to climb again. It’s crucial to analyze these trends to predict future changes.
Current Market Trends and Predictions
Currently, mortgage rates remain relatively low compared to previous years. This has led to a competitive housing market, with many buyers taking advantage of the favorable rates. However, experts predict that rates may start to rise in the near future as the economy continues to improve. It’s essential for potential homebuyers to stay informed about these market trends.
External Factors Influence
External factors such as inflation and economic growth play a significant role in determining mortgage rates. Inflation leads to higher interest rates, while economic growth can also impact rates. For instance, a strong economy may result in increased demand for loans, causing rates to rise. Understanding these factors is key to making informed decisions when it comes to obtaining a mortgage.
Refinancing and Interest Rates
Refinancing a mortgage involves replacing your current home loan with a new one, usually to take advantage of lower interest rates. This can potentially lower your monthly payments, reduce the total interest paid over the life of the loan, or shorten the loan term.
Considerations for Refinancing
- Current Interest Rates: One of the main considerations is whether the current interest rates are lower than the rate on your existing mortgage. A significant decrease in rates could make refinancing a smart financial move.
- Loan Term: Refinancing may also be beneficial if you want to change the length of your loan term. For example, switching from a 30-year mortgage to a 15-year mortgage can save you money on interest in the long run.
- Closing Costs: It’s essential to consider the closing costs associated with refinancing. These costs can include application fees, appraisal fees, and other charges. Make sure the potential savings from refinancing outweigh these costs.
Examples of Refinancing Decisions
- Good Decision: If you have a high-interest rate on your current mortgage and the market rates have dropped significantly, refinancing can help you save money over the life of the loan.
- Bad Decision: If you plan to move in a few years, the costs of refinancing might outweigh the savings from lower interest rates. In this case, it may not make financial sense to refinance.
