Yo, diving into the world of financial yield calculation, where numbers meet strategy and decisions. Let’s break it down and see how it all adds up, one calculation at a time.
From understanding the basics to exploring real-world examples, get ready to level up your investment game with this essential knowledge.
Introduction to Financial Yield Calculation
Financial yield calculation is a crucial aspect of investment analysis that helps investors assess the return on their investments. It is important to understand how to calculate yield as it provides valuable insights into the profitability of an investment.
The basic concept of yield is the return on an investment over a specific period, expressed as a percentage of the initial investment. Yield can be calculated in different ways depending on the type of financial instrument, such as bonds, stocks, or real estate.
Types of Financial Instruments for Yield Calculation
When it comes to financial instruments, yield calculation plays a significant role. Here are some examples:
- Bonds: Yield calculation for bonds involves considering factors like coupon payments, bond price, and maturity date to determine the overall return on investment.
- Stocks: Dividend yield is a common metric used to calculate the return on investment in stocks, taking into account the dividends paid by the company.
- Real Estate: Rental yield is used to calculate the return on investment in real estate properties, considering factors like rental income and property value.
Types of Financial Yields
Financial yields play a crucial role in evaluating the return on investment for various financial instruments. Different types of financial yields provide insights into different aspects of investment performance. Let’s explore some common types of financial yields and how they are calculated.
Current Yield
The current yield is a straightforward measure of return that calculates the annual income generated by an investment relative to its current market price. It is calculated as follows:
Current Yield = Annual Interest Income / Current Market Price
For example, if a bond pays $50 in annual interest and its current market price is $1,000, the current yield would be 5% ($50 / $1,000).
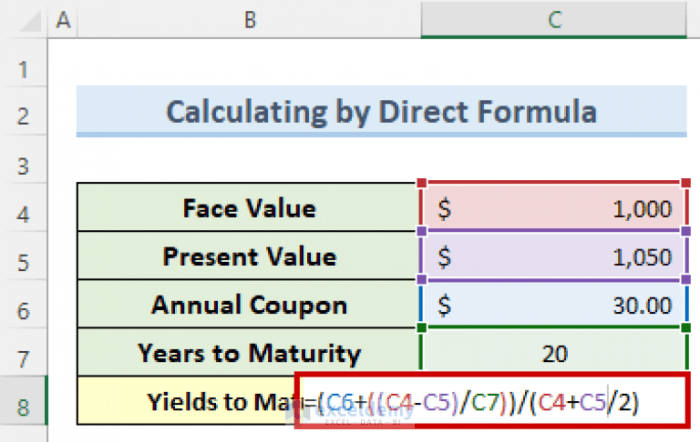
Yield to Maturity
Yield to maturity (YTM) is a more comprehensive measure that takes into account the total return on a bond if held until maturity. It considers not only the annual interest income but also any capital gains or losses due to price changes. The calculation for YTM is more complex and often requires the use of financial calculators or software.
Dividend Yield
Dividend yield is a measure of the annual dividend income generated by a stock relative to its current market price. It is calculated as follows:
Dividend Yield = Annual Dividends per Share / Current Market Price
For example, if a stock pays $2 in annual dividends and its current market price is $50, the dividend yield would be 4% ($2 / $50).
Comparison of Calculation Methodology
While current yield and dividend yield are relatively straightforward to calculate, yield to maturity involves more complex computations that consider the time value of money and present value of future cash flows. Each type of yield provides unique insights into the investment’s performance and helps investors make informed decisions based on their investment goals.
Factors Influencing Financial Yield Calculation
When calculating financial yields, several key factors come into play that can significantly impact the final results. Factors such as interest rates, market conditions, time to maturity, risk levels, and credit ratings all play a crucial role in determining the yield of an investment.
Interest Rates
Interest rates have a direct impact on financial yield calculations. When interest rates rise, the yield on existing investments may decrease as newer investments offer higher yields. Conversely, when interest rates fall, the yield on existing investments may increase as they become more attractive compared to newer investments.
Market Conditions
Market conditions, including economic indicators and overall market performance, can influence yield calculations. Positive market conditions usually lead to lower yields, as investors are willing to accept lower returns in a thriving market. On the other hand, in uncertain or volatile market conditions, investors may demand higher yields to compensate for increased risk.
Time to Maturity
The time to maturity of an investment is another crucial factor in yield calculations. Generally, investments with longer maturities tend to offer higher yields to investors. This is because longer-term investments are exposed to more risks and uncertainties, thus requiring a higher yield to compensate for the extended holding period.
Risk Levels and Credit Ratings
The risk levels associated with an investment, as well as its credit ratings, can significantly impact yield calculations. Investments with higher risk levels or lower credit ratings usually offer higher yields to investors to offset the increased risk of default. Conversely, investments with lower risk levels or higher credit ratings may have lower yields due to their perceived stability and security.
Importance of Financial Yield Calculation in Decision Making
Financial yield calculation plays a crucial role in helping investors make informed decisions about their investments. By analyzing the yield of different investment options, investors can assess the potential returns and risks associated with each option, allowing them to make strategic decisions that align with their financial goals.
Significance of Yield Analysis in Portfolio Management
Yield analysis is essential in portfolio management as it helps investors evaluate the performance of their investments and make adjustments accordingly. By comparing the yields of different assets within a portfolio, investors can identify underperforming assets and reallocate their investments to potentially higher-yielding options. This proactive approach to portfolio management can help investors optimize their returns and minimize risks.
- Yield analysis allows investors to track the performance of their investments over time, helping them identify trends and patterns that can inform future investment decisions.
- By assessing the yield of various investment options, investors can calculate the risk-adjusted returns of each option, enabling them to make more informed decisions based on their risk tolerance.
- Comparing the yields of different assets can help investors diversify their portfolios effectively, spreading risk across different asset classes and potentially increasing overall returns.
It is essential for investors to regularly conduct yield analysis to ensure their investment portfolio remains aligned with their financial objectives.
Examples of Using Yield Calculations for Comparison and Risk Assessment
Yield calculations can be used in various ways to compare investment options and assess risks. For example, when comparing two bonds with different yields, investors can calculate the yield to maturity (YTM) to determine which bond offers a higher return after accounting for the differences in coupon payments and maturity dates. Additionally, yield calculations can help investors assess the risk associated with different investment options by calculating metrics such as the Sharpe ratio or the standard deviation of returns.
- Calculating the dividend yield of stocks can help investors compare the income generated from different stocks and identify high-yielding opportunities.
- Assessing the yield spread between corporate bonds and government bonds can provide insights into the credit risk associated with each bond type.
- Using the current yield of a bond to evaluate the income potential relative to its current market price can help investors make informed decisions about bond investments.
