Capital gains tax sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality. Get ready to dive into the world of finance with a twist of American high school hip style.
As we unravel the complexities of capital gains tax, you’ll gain a deeper understanding of how this tax impacts your financial decisions and investments.
What is Capital Gains Tax?
Capital gains tax is a tax levied on the profits earned from the sale of assets such as stocks, real estate, or valuable items. It is designed to tax the increase in value of these assets over time.
Assets Subject to Capital Gains Tax
- Stocks and bonds
- Real estate properties
- Artwork and collectibles
- Businesses
Factors Affecting Capital Gains Tax Rates
- Duration of ownership: Assets held for over a year may qualify for lower long-term capital gains tax rates.
- Income level: Higher-income individuals may face higher capital gains tax rates.
- Type of asset: Different assets may be subject to varying tax rates based on specific regulations.
- Tax bracket: Capital gains tax rates can be influenced by the taxpayer’s overall income tax bracket.
Calculating Capital Gains Tax
When it comes to calculating capital gains tax, it’s essential to understand the difference between short-term and long-term capital gains tax rates. Short-term capital gains tax applies to assets held for one year or less, while long-term capital gains tax applies to assets held for more than one year.
Short-term vs. Long-term Capital Gains Tax Rates
Short-term capital gains are taxed at ordinary income tax rates, which can range from 10% to 37%, depending on your tax bracket. On the other hand, long-term capital gains are taxed at lower rates, typically 0%, 15%, or 20%, based on your income level.
Calculating Capital Gains Tax on the Sale of an Asset
To calculate capital gains tax on the sale of an asset, follow these steps:
- Determine the purchase price of the asset.
- Calculate the sale price of the asset.
- Find the cost basis by subtracting any expenses related to the sale from the purchase price.
- Subtract the cost basis from the sale price to determine the capital gain.
- Apply the appropriate tax rate based on whether it’s a short-term or long-term capital gain.
- Report the capital gain on your tax return and pay the applicable taxes.
Strategies to Minimize Capital Gains Tax
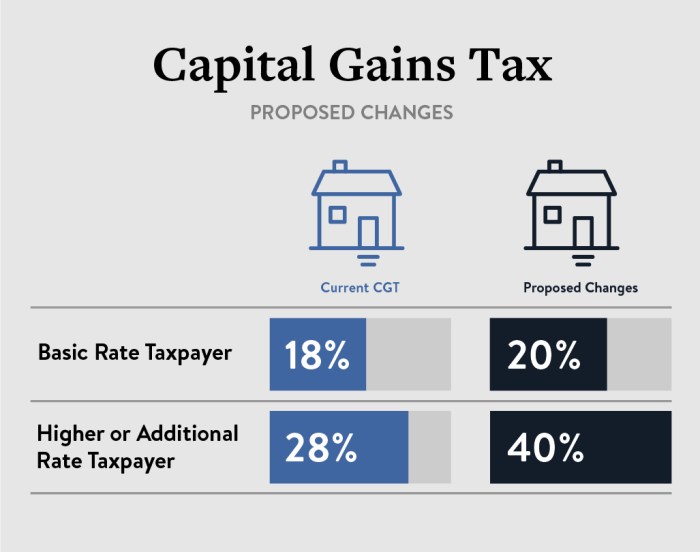
When it comes to minimizing capital gains tax, there are several legal strategies individuals can use to lower their tax burden and maximize their investment returns. By taking advantage of tax-saving investment options and understanding the different ways to reduce capital gains tax liability, investors can optimize their financial outcomes.
Tax-Saving Investment Options
- Utilize tax-advantaged accounts such as Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs) or 401(k) plans to defer taxes on capital gains until retirement.
- Consider investing in tax-exempt municipal bonds or index funds, which can provide income that is not subject to capital gains tax.
- Harvest tax losses by selling investments at a loss to offset capital gains and reduce taxable income.
Legal Ways to Reduce Capital Gains Tax Liability
- Hold investments for the long term to qualify for lower tax rates on capital gains, known as long-term capital gains tax rates.
- Take advantage of the annual capital gains tax exclusion by gifting appreciated assets to family members who are in a lower tax bracket.
- Invest in Opportunity Zones to defer or potentially reduce capital gains tax on investments in designated economically distressed areas.
Comparing Different Strategies
- While tax-advantaged accounts offer tax deferral benefits, they have contribution limits and restrictions on withdrawals.
- Tax-exempt investments may provide a steady income stream without incurring capital gains tax, but returns may be lower compared to taxable investments.
- Tax-loss harvesting can be an effective way to offset gains and reduce tax liability, but it requires careful monitoring of investment performance.
Impact of Capital Gains Tax on Investments
When it comes to investments, the impact of capital gains tax cannot be overlooked. This tax has a significant influence on the decisions investors make and the overall returns they receive on their investments. Understanding how capital gains tax affects investment portfolios is crucial for maximizing profits and minimizing tax liabilities.
Implications of Capital Gains Tax on Stock Market Investments
Investing in the stock market can be a lucrative venture, but capital gains tax plays a crucial role in determining the net gains investors receive. When investors sell stocks at a profit, they are subject to capital gains tax on the realized gains. The tax rate can vary based on how long the stocks were held before being sold.
- Short-term Capital Gains: Stocks held for less than a year are subject to short-term capital gains tax, which is typically taxed at a higher rate compared to long-term capital gains.
- Long-term Capital Gains: Stocks held for more than a year qualify for long-term capital gains tax, which is usually taxed at a lower rate, incentivizing investors to hold onto their investments for a longer period.
Understanding the tax implications of stock market investments is essential for investors to make informed decisions and optimize their investment strategies.
Real-World Examples of Capital Gains Tax Impact on Investment Portfolios
Let’s consider a scenario where an investor purchases shares of a company and sells them after two years, realizing a significant gain. The investor will be subject to long-term capital gains tax on the profits earned from the sale. By factoring in the tax implications, the investor can assess the after-tax returns and make adjustments to their investment strategy accordingly.
Additionally, changes in capital gains tax rates by the government can have a direct impact on investment decisions. Investors may choose to sell or hold onto their investments based on the anticipated tax implications, showcasing the influence of tax policies on investment behavior.
