Yo, ready to dive into the world of REITs? Buckle up as we break down what these bad boys are all about and why you should care. From the basics to the nitty-gritty, we got you covered.
Introduction to REITs
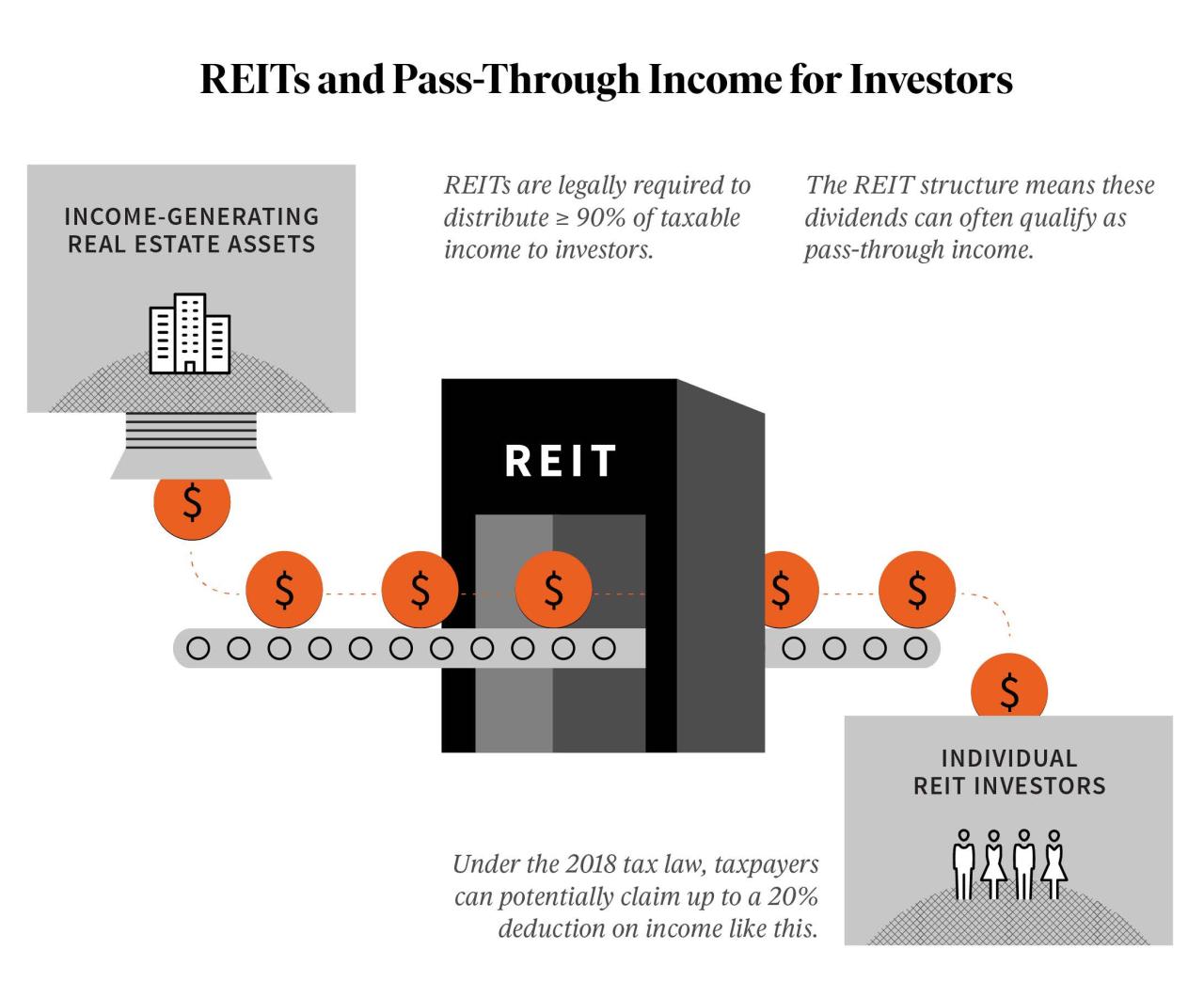
Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) are companies that own, operate, or finance income-producing real estate across a range of property sectors. They allow individuals to invest in real estate without having to buy, manage, or finance any properties themselves.
REITs are structured in a way that requires them to distribute at least 90% of their taxable income to shareholders in the form of dividends. This structure provides investors with a steady income stream and potential for capital appreciation through property value increases.
Purpose and Structure of REITs
REITs provide investors with the opportunity to invest in real estate without the challenges of property ownership, such as property management and maintenance. They also offer diversification benefits by allowing investors to spread their investment across various real estate sectors, such as residential, commercial, healthcare, and hospitality.
The structure of REITs as pass-through entities helps them avoid corporate income tax, making them attractive for investors seeking high dividend yields and potential for long-term growth. Additionally, REITs are required to follow strict regulations and guidelines set by the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) to ensure transparency and investor protection.
Benefits of Investing in REITs
- High Dividend Yields: REITs are known for their high dividend yields due to their income distribution requirements.
- Liquidity: Investing in REITs provides investors with liquidity as shares can be bought and sold easily on the stock exchange.
- Diversification: REITs offer investors the opportunity to diversify their investment portfolio across different real estate sectors and geographic locations.
- Professional Management: REITs are managed by experienced professionals who handle property operations and strategic decision-making.
- Tax Advantages: Investors in REITs can benefit from potential tax advantages, such as pass-through taxation and tax-deferred distributions.
Types of REITs
When it comes to Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs), there are different types that investors can consider. These include equity REITs, mortgage REITs, and hybrid REITs. Each type has its own unique characteristics and investment opportunities.
Equity REITs
Equity REITs are the most common type of REITs and they primarily invest in and own income-producing real estate properties. These properties can range from residential buildings to shopping centers, office buildings, and more. Equity REITs generate income through rental payments from tenants and can provide investors with dividends from the rental income.
Popular examples of equity REITs include Simon Property Group (SPG), which focuses on shopping malls, and AvalonBay Communities (AVB), which specializes in apartment buildings.
Mortgage REITs
Mortgage REITs, also known as mREITs, do not own physical properties like equity REITs. Instead, they invest in mortgage-backed securities or provide financing for real estate loans. Mortgage REITs generate income through interest on the loans they provide and can be more sensitive to interest rate changes.
An example of a popular mortgage REIT is Annaly Capital Management (NLY), which invests in mortgage-backed securities and other mortgage-related assets.
Hybrid REITs
Hybrid REITs combine elements of both equity and mortgage REITs. They invest in a mix of physical properties and real estate loans, offering investors a diversified portfolio. Hybrid REITs can provide a balance of rental income and interest income.
One example of a hybrid REIT is Realty Income Corporation (O), which invests in commercial properties and has a history of paying consistent dividends to investors.
Investors can choose among these different types of REITs based on their investment goals and risk tolerance. Each type offers a unique way to access the real estate market and can provide opportunities for income and capital appreciation.
Investing in REITs
Investing in Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) can be a great way to diversify your investment portfolio and potentially earn passive income.
The Process of Investing in REITs
Investing in REITs is similar to investing in stocks. You can buy shares of publicly traded REITs through a brokerage account. Some REITs may also offer direct investment options. Keep in mind that REITs are required by law to distribute at least 90% of their taxable income to shareholders in the form of dividends.
Potential Risks Associated with Investing in REITs
While REITs can offer attractive dividends and potential capital appreciation, they also come with risks. These risks include interest rate sensitivity, economic downturns impacting real estate values, and specific risks related to the type of real estate the REIT invests in.
Comparing Returns of Investing in REITs versus Other Investment Options
When comparing returns, it’s important to consider that REITs typically offer higher dividend yields compared to stocks. However, the total returns from REITs may not always outperform other investment options like stocks or bonds. It’s essential to assess your risk tolerance and investment goals before deciding to invest in REITs.
Factors to Consider
When investing in REITs, there are several key factors to consider to make informed decisions and maximize returns. One must assess various economic factors and understand the impact of interest rates on REIT performance.
Economic Factors Impacting REIT Investments
- Market Conditions: The overall economic environment, including GDP growth, unemployment rates, and consumer spending, can significantly influence REIT performance.
- Real Estate Market Trends: Understanding the current state of the real estate market, such as supply and demand dynamics, rental rates, and property values, is crucial for making informed investment decisions.
- Regulatory Environment: Changes in regulations related to real estate, taxation, or zoning laws can impact REITs and their ability to generate returns.
Impact of Interest Rates on REIT Performance
- Interest Rate Sensitivity: REITs are sensitive to interest rate changes, as they often rely on debt to finance their property acquisitions. When interest rates rise, borrowing costs increase, which can negatively affect REIT profitability.
- Dividend Yields: Higher interest rates can lead to a decrease in REIT dividend yields, making them less attractive to income-seeking investors.
- Property Valuations: Rising interest rates can also impact property valuations, potentially affecting the overall performance of REITs.
Diversification with REITs
Investing in Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) can play a crucial role in diversifying an investment portfolio. By adding REITs to your investment mix, you can spread out your risk and potentially enhance your overall returns.
Complementing Other Investment Assets
- REITs can provide a source of passive income through dividends, which can complement growth-oriented investments like stocks.
- They often have a low correlation with traditional asset classes such as stocks and bonds, making them a valuable addition for diversification.
- Real estate as an asset class tends to behave differently from the stock market, offering a hedge against market volatility.
Role in a Well-Balanced Investment Strategy
- REITs can act as a stabilizing force in a portfolio, especially during times of economic downturns when other investments may be underperforming.
- They provide exposure to the real estate market without the need for direct property ownership, offering liquidity and ease of diversification.
- Including REITs in a diversified portfolio can help reduce overall risk and potentially improve risk-adjusted returns over the long term.
Tax Implications
Investing in Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) comes with its own set of tax advantages and implications that investors should be aware of. Understanding how REIT dividends are taxed differently compared to other investments can help you optimize tax benefits when incorporating REITs into your investment portfolio.
Tax Advantages of REITs
- REITs are required by law to distribute at least 90% of their taxable income to shareholders in the form of dividends, which helps them avoid corporate income tax.
- Investors can benefit from favorable tax treatment on these dividends, as they are taxed at the individual’s ordinary income tax rate, which can be lower than the tax rate on capital gains.
Tax Implications of REIT Dividends
- Unlike dividends from traditional stocks, REIT dividends are not qualified dividends, so they do not qualify for the lower tax rates that apply to qualified dividends.
- REIT dividends are generally taxed as ordinary income, which means they are subject to the individual’s marginal tax rate.
Optimizing Tax Benefits with REITs
- Consider holding REITs in tax-advantaged accounts like a Roth IRA or 401(k) to avoid immediate taxation on dividends.
- Utilize tax-loss harvesting strategies to offset gains from REIT investments with losses from other investments, reducing your overall tax liability.
- Consult with a tax professional to navigate the complexities of REIT taxation and develop a tax-efficient investment strategy.
